Unlocking Precision: How Automated CNC Milling Machines Are Revolutionizing Mold Making
- Share
- Issue Time
- Dec 27,2025
Summary
Automated CNC milling machines, particularly 5-axis and 6-axis systems, are transforming mold making with superior precision, ability to machine complex geometries in one setup, reduced lead times, enhanced surface finishes, and seamless CAD/CAM integration. These advancements benefit industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical while promoting sustainability and smart manufacturing.
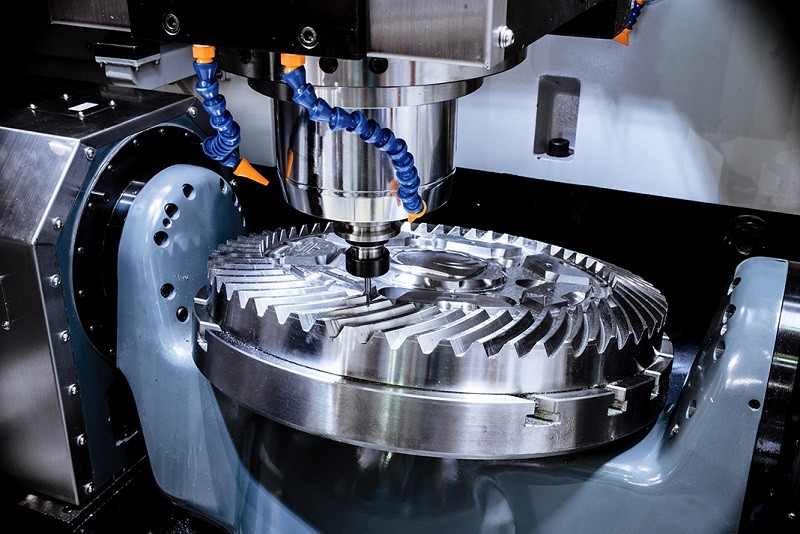

Unlocking Precision: How Automated CNC Milling Machines Are Revolutionizing Mold Making
In the heart of modern manufacturing, the quality of a final product is fundamentally tied to the precision of the tool that creates it. For industries from automotive and aerospace to medical devices and consumer electronics, that tool is the mold. The journey of creating high-quality, durable, and complex molds has been revolutionized by one technology above all: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machining. Automated CNC milling machines, particularly advanced 5-axis and 6-axis systems, are the backbone of modern mold making, offering a level of accuracy, speed, and complexity that was once unimaginable.
This technology has moved beyond simple automation; it integrates sophisticated software, robotics, and advanced engineering to turn digital blueprints into physical tools with micron-level precision. The impact is profound, enabling manufacturers to shorten development cycles, reduce costs, and produce parts with flawless consistency.

What is Automated CNC Milling for Mold Making?
Automated CNC milling is a subtractive manufacturing process where computer-controlled machines use rotating cutting tools to precisely remove material from a workpiece, shaping it into a mold. The process begins with a Computer-Aided Design (CAD) model, which is translated by Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software into G-code—a set of instructions that dictates every movement of the machine. This seamless digital workflow eliminates the manual errors and limitations of traditional methods, enabling the creation of highly complex and precise molds that can withstand the rigors of mass production. Molds are typically machined from durable materials like tool steel or aluminum to ensure they maintain their integrity over thousands of cycles.
The Leap from 3-Axis to 5-Axis Machining
A standard 3-axis CNC machine operates on the X, Y, and Z linear axes. While effective for simpler parts, it requires multiple setups to machine different sides of a complex mold, introducing the risk of errors with each repositioning. 5-axis CNC machining solves this by adding two rotational axes (A and C, or B and C), allowing the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from virtually any angle in a single setup. This capability is a game-changer for mold making, as it allows for the efficient creation of intricate cavities, deep pockets, and complex curved surfaces without compromising accuracy.
Why 5-Axis Technology is a Game-Changer for Molds
The adoption of 5-axis CNC machines has brought transformative benefits to the mold making industry. By enabling the machining of complex geometries in a single setup, these machines drastically reduce the accumulated errors from multiple setups. This single-setup approach not only tightens tolerances but also significantly cuts down on overall production time. Furthermore, 5-axis machines can use shorter, more rigid cutting tools because they can tilt the tool or the workpiece to avoid collisions. Shorter tools are less prone to vibration, resulting in a superior surface finish that often eliminates the need for time-consuming and costly manual polishing.
Exploring the Sixth Axis: Pushing the Boundaries of Complexity
While 5-axis machining is the standard for high-complexity work, 6-axis CNC machines offer even greater flexibility. The sixth axis adds another rotational capability, often seen in robotic arms with a spindle attached. While these systems may lack some of the rigidity of a traditional 5-axis machining center, they offer unparalleled freedom of movement. This makes them ideal for tasks like trimming large composite molds or for hybrid manufacturing processes that combine additive and subtractive techniques. For mold makers, the primary advantage of a 6th axis can be a significant reduction in cutting times—in some cases by up to 75% compared to 5-axis setups—by optimizing tool transitions and movements.
Core Benefits of Automated CNC Milling in Mold Manufacturing
The advantages of using automated multi-axis CNC machines for mold production are clear and substantial. These benefits directly impact efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness across the board.
| Feature | Benefit in Mold Making |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Precision | Achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.001 mm, crucial for high-quality, consistent molded parts. |
| Increased Complexity | Manufactures intricate geometries, undercuts, and deep cavities in a single setup. |
| Superior Surface Finish | The ability to use shorter tools and maintain an optimal cutting angle reduces tool marks, minimizing manual polishing. |
| Reduced Lead Times | Single-setup machining and faster cutting speeds can shorten mold development cycles by 40% or more. |
| Enhanced Tool Life | Maintaining an ideal tool orientation reduces wear and tear, extending the life of expensive cutting tools. |
The Crucial Role of CAD/CAM Software
The power of an automated CNC machine is unlocked by its software. Advanced CAD/CAM systems are essential for mold making. They not only assist in designing the mold with features like draft angles and parting lines but also simulate the entire machining process. This simulation allows programmers to detect and avoid potential collisions between the tool, workpiece, and machine components. Modern CAM software also includes specialized toolpaths, such as high-speed machining and adaptive milling, which optimize material removal rates while protecting the tool and ensuring a high-quality finish.
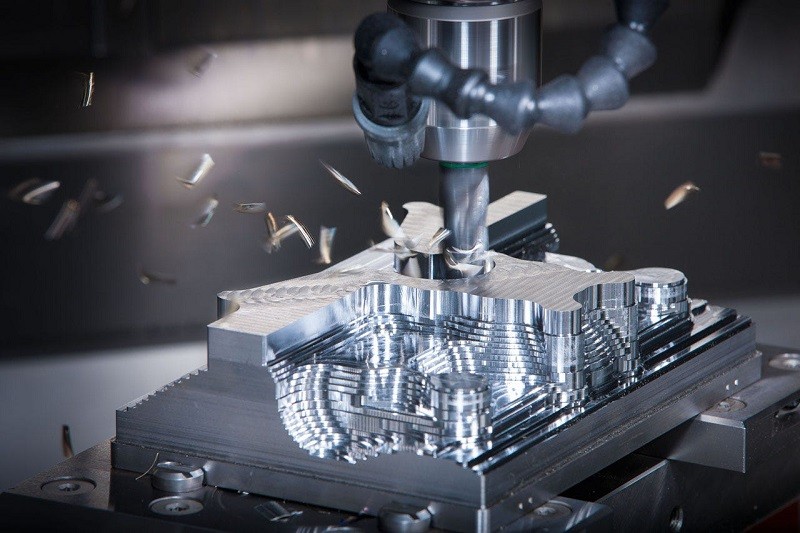
Key Industries Driving Demand for Automated Mold Making
Several key industries rely heavily on the precision and complexity afforded by automated CNC milling for molds. In the automotive sector, these machines create large molds for bumpers, dashboards, and engine components. The aerospace industry uses them for high-precision molds for composite parts like fuselage panels and turbine blades. In the medical field, they are indispensable for producing molds for surgical instruments and life-saving implants, where accuracy is paramount.
Automation Beyond the Cut: Streamlining the Entire Workflow
True automation in mold making extends beyond the milling process itself. Modern workshops are integrating robotic systems to handle loading and unloading of workpieces and finished molds, allowing for 24/7 unattended operation. Furthermore, on-machine verification (OMV) systems use probes to inspect the mold's dimensions during the machining process. This real-time feedback allows the machine to make automatic adjustments, ensuring the final part is within tolerance without removing it from the machine, saving valuable time and preventing errors.
The Rise of Sustainable and Smart Manufacturing
Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in manufacturing. Automated CNC machines contribute to greener production by optimizing toolpaths to reduce energy consumption and minimize material waste. The precision of CNC also reduces the rate of scrapped parts. Concurrently, the integration of IoT (Internet of Things) and AI is paving the way for smart manufacturing. CNC machines equipped with sensors can monitor their own health, predict maintenance needs, and provide real-time production data, leading to a more efficient, resilient, and connected workflow.
Training the Workforce for a High-Tech Future
As CNC technology becomes more sophisticated, so does the need for a skilled workforce. The mold maker of the future is not just a manual machinist but a highly trained technician proficient in CAD/CAM programming, robotics, and data analysis. Continuous training and workforce development are essential for companies looking to harness the full potential of automated manufacturing and maintain a competitive edge. This shift requires a focus on both technical and problem-solving skills to manage these complex, integrated systems.
Conclusion: The Future of Mold Making is Automated and Precise
Automated CNC milling has fundamentally redefined the standards of mold manufacturing. By enabling the production of highly complex, precise, and durable molds with unprecedented speed and consistency, this technology has become a cornerstone of modern industry. From 5-axis systems that master intricate geometries to the integration of robotics and AI, the journey toward fully autonomous and intelligent mold making is well underway. For manufacturers, embracing these advancements is no longer just an option—it is the key to unlocking innovation, driving efficiency, and shaping the future of production.