On-Demand Manufacturing: Transforming Production for CNC Milling Parts Manufacturers
- Share
- Issue Time
- Dec 25,2025
Summary
On-demand manufacturing, also known as custom or cloud manufacturing, is revolutionizing the CNC milling industry by shifting from traditional mass production to an agile, responsive model. This approach allows manufacturers to produce custom parts with unprecedented speed, precision, and scalability.

As an experienced CNC milling parts manufacturer, I've seen firsthand how the industry has been reshaped by technological advancements. One of the most significant shifts has been the rise of on-demand manufacturing (ODM). This innovative approach, also known as custom or cloud manufacturing, is revolutionizing how products are made, moving away from traditional mass production towards a more agile, responsive model.
On-demand manufacturing, particularly when powered by sophisticated CNC machining, allows us to produce custom parts with unprecedented speed, precision, and scalability. This blog post will explore the ins and outs of on-demand manufacturing for CNC milling parts manufacturers, diving into its benefits, challenges, and how it's transforming the production landscape.

What On-Demand Manufacturing Means for CNC Milling Parts Manufacturers
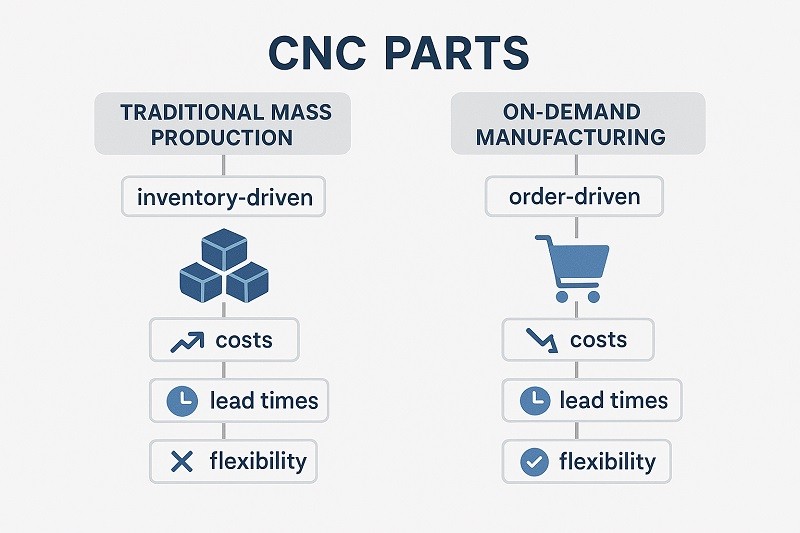
The shift towards on-demand production represents a fundamental change in manufacturing philosophy. Instead of producing large quantities of parts based on market forecasts—a "push" system—on-demand manufacturing operates on a "pull" system. This means production is initiated only after a customer places a confirmed order, ensuring that every part manufactured is already sold. This model leverages digital technologies to connect customer needs directly with manufacturing capacity, creating a more efficient, flexible, and customer-centric production environment.
Defining On-Demand for CNC Milling Parts
At its core, on-demand manufacturing for CNC milling parts is a production system where components are created precisely when needed and in the exact quantities required. This "made-to-order" approach stands in stark contrast to traditional methods that involve mass-producing and storing large volumes of inventory. For CNC milling, this means a customer can order a single, highly complex prototype or a small batch of custom components without the economic constraints of conventional manufacturing. The model is built on agility and responsiveness, using digital tools to streamline the entire process from design submission to final delivery.
This approach is sometimes referred to as custom manufacturing or cloud manufacturing, highlighting its reliance on digital networks and its ability to produce bespoke products aligned with unique specifications. By eliminating the need for vast storage facilities and the financial risk of unsold inventory, on-demand manufacturing provides a lean and efficient alternative for modern businesses. It empowers companies to react swiftly to market changes and customer demands with unparalleled precision.
How On-Demand Production Works in CNC Milling
The on-demand production workflow for CNC milling is a testament to the power of digital integration. The entire process is streamlined to minimize delays and maximize efficiency, moving from a digital concept to a physical part in a remarkably short timeframe.
Here is a typical step-by-step breakdown of the process:
- Digital Design Submission: The process begins when a customer uploads a 3D model of their part, typically created using Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software. This digital file contains all the geometric information needed for production.
- Automated Quoting: Many on-demand platforms use AI-powered software to instantly analyze the CAD file, assess its manufacturability, and generate a quote based on factors like material, complexity, and quantity. This eliminates the lengthy back-and-forth often associated with traditional quoting.
- Order Confirmation and CAM Programming: Once the customer confirms the order, the digital file is processed by Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software. This software converts the 3D model into a set of machine-readable instructions, known as G-code, which dictates the precise movements of the CNC machine's cutting tools.
- Automated Machining: The G-code is sent to an available CNC milling machine. The machine then autonomously executes the program, cutting away material from a solid block of metal or plastic to create the final part with extreme precision. Advanced machines can operate with minimal human oversight, sometimes around the clock.
- Quality Control and Inspection: After machining, the finished parts undergo a rigorous quality inspection to ensure they meet the exact specifications and tolerances defined in the original design. This can involve an array of metrology tools, from digital calipers to Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs).
- Shipping and Delivery: The parts are then packaged and shipped directly to the customer, often within days of the initial order. The entire workflow is managed through a centralized platform, providing transparency and real-time updates.

The Impact on Traditional Mass Production
On-demand manufacturing directly challenges the long-standing principles of traditional mass production. While mass production thrives on economies of scale—where producing higher volumes leads to a lower cost per unit—it is inherently rigid and requires significant upfront investment in tooling and storage. On-demand manufacturing, however, is built for flexibility and customization, making it economically viable to produce low-to-medium volume batches or even single parts.
The table below highlights the key differences between these two production models:
| Feature | Traditional Mass Production | On-Demand Manufacturing (CNC Milling) |
|---|---|---|
| Production Trigger | Forecast-based ("Push") | Order-based ("Pull") |
| Volume | High volume, low mix | Low to high mix, variable volume |
| Inventory | Large stockpiles of finished goods | Minimal to zero finished goods inventory |
| Upfront Costs | High (molds, dies, tooling) | None to very low (no custom tooling) |
| Lead Times | Weeks or months | Days or even hours |
| Customization | Limited and costly | High and cost-effective |
| Financial Risk | High risk from unsold inventory and obsolescence | Low risk, as production is tied to demand |
| Best For | Stable, high-demand, standardized products. | Prototypes, custom parts, market testing, and unpredictable demand. |
This shift does not necessarily mean the end of mass production, which remains the most cost-effective method for millions of identical items. Instead, on-demand manufacturing serves as a powerful and complementary model. It excels in scenarios where agility, customization, and speed are critical, such as in rapid prototyping, new product introduction, and serving niche markets with specialized needs. For CNC milling parts manufacturers, this hybrid approach allows them to serve a much broader range of client needs, from a one-off custom fixture to a recurring small-batch production run.
Key Advantages for CNC Milling Parts Manufacturers in the On-Demand Era
Adopting an on-demand manufacturing model unlocks a host of strategic advantages for CNC milling parts manufacturers. This modern approach to production not only enhances operational efficiency but also provides a significant competitive edge in a market that increasingly values speed, personalization, and agility. By shifting away from forecast-based mass production, manufacturers can align their operations more closely with actual customer demand, leading to smarter resource allocation and improved business outcomes.
Reduced Costs and Waste for CNC Milling Parts
One of the most significant benefits of on-demand manufacturing is the drastic reduction in costs and waste. Traditional manufacturing often leads to substantial expenses tied up in inventory, including storage, management, and the risk of obsolescence. On-demand production virtually eliminates these costs by ensuring parts are made only when an order is confirmed. This "just-in-time" approach frees up capital that would otherwise be locked in unsold stock. [1_1, 10]
Furthermore, the precision of CNC machining inherent in this model plays a crucial role in minimizing material waste. By working directly from a digital design, the subtractive process is highly optimized to remove only the necessary material from a raw block. Advanced CAM software can also calculate the most efficient toolpaths and nest multiple parts on a single piece of stock to maximize material utilization. This focus on efficiency not only lowers raw material costs but also supports sustainability goals by reducing a company's environmental footprint. Energy consumption is also lowered, as machines run only when necessary to fulfill active orders rather than operating continuously to build up inventory.
Enhanced Customization and Flexibility for CNC Milling Parts
On-demand manufacturing gives CNC milling parts manufacturers unparalleled flexibility to meet a wide array of customer needs. The model is perfectly suited for producing highly customized parts tailored to specific functions or complex assemblies. Unlike traditional methods that require expensive and time-consuming retooling for any design modification, CNC machining allows for quick changes to be made by simply updating the digital CAD file. This empowers clients to order components that perfectly match their requirements, whether it's for unique geometries, specific material properties, or intricate features.
This adaptability is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, enabling factories to respond to diverse production demands with minimal downtime or manual intervention. Whether a customer needs a single prototype to test a new concept or a small batch of specialized parts for a niche application, on-demand CNC machining can deliver with speed and precision. This flexibility extends to material selection, as manufacturers can easily switch between various metals, plastics, and composites to meet specific performance requirements. Industries such as aerospace, medical, and automotive, which demand high-quality, customized parts that meet strict standards, benefit immensely from this level of personalization.
Faster Time-to-Market and Risk Mitigation for CNC Milling Parts
In today's fast-paced market, speed is a critical competitive advantage. On-demand manufacturing dramatically accelerates the product development cycle, significantly reducing the time it takes to get a product from concept to market. The streamlined, digital workflow—from instant quoting and automated programming to rapid machining—eliminates many of the bottlenecks inherent in traditional procurement. This allows companies to turn around high-quality parts in days instead of weeks or months, enabling quicker design iterations and faster product validation.
This speed is intrinsically linked to risk mitigation. For startups and businesses launching new products, on-demand manufacturing offers a low-risk way to test market viability. Instead of committing a large capital investment to mass production for an unproven idea, companies can order small batches to gauge consumer interest. This approach minimizes financial exposure by avoiding the problem of unsold inventory if a product fails to gain traction. Strategic prototyping using CNC machining also helps identify and resolve potential design flaws early in the development process, preventing costly tooling errors and production delays down the line. By making the manufacturing supply chain more nimble and responsive, on-demand production helps companies capitalize on opportunities and navigate market uncertainty with greater confidence.
Navigating the Challenges of On-Demand CNC Milling Parts Production
While the on-demand model offers transformative benefits, it also presents a unique set of challenges that CNC milling parts manufacturers must navigate. The very nature of producing custom parts in low volumes introduces complexities related to cost, scheduling, and quality assurance. Successfully implementing an on-demand strategy requires a clear understanding of these hurdles and the adoption of robust processes to overcome them. Addressing these issues proactively is key to unlocking the full potential of this agile production method and delivering consistent value to clients.
Addressing Higher Unit Costs in On-Demand CNC Milling Parts
A primary challenge of on-demand manufacturing is that the cost per unit is often higher compared to traditional mass production. This is due to the absence of economies of scale; setup costs, programming time, and labor are spread across a small number of parts, or even a single component. Traditional methods, like injection molding, involve high upfront tooling costs but become extremely cost-effective per part when producing thousands or millions of identical items.
However, it's crucial to evaluate cost from a total project perspective rather than just the per-unit price. While the individual part may cost more, on-demand production eliminates expenses related to:
- Inventory and Warehousing: There are no costs for storing, managing, or insuring large stockpiles of unsold goods.
- Tooling: For CNC machining, there are no expensive molds or dies to create, drastically reducing initial investment.
- Waste: The risk of inventory becoming obsolete due to design changes or shifting market demand is eliminated.
To manage higher unit costs, manufacturers can implement several strategies. Optimizing designs for manufacturability (DFM) by simplifying geometries, using standard tool sizes, and specifying tolerances only where necessary can significantly reduce machining time and expense. By communicating these trade-offs clearly, manufacturers can help clients understand that the higher unit price is balanced by greater flexibility, lower overall financial risk, and faster speed to market.
Managing Lead Times and Scalability for CNC Milling Parts
Although on-demand manufacturing is celebrated for its speed, managing lead times can still be a challenge. Customers often expect near-instant delivery, but production timelines are influenced by several factors, including part complexity, material availability, machine capacity, and the current production queue. A complex part requiring multi-axis machining and special finishing will naturally take longer than a simple 3-axis component. Furthermore, sourcing specialized or exotic materials can introduce significant delays, creating a bottleneck before machining even begins.
Scalability presents another critical hurdle. A system designed for producing one-off prototypes and low-volume orders can be quickly overwhelmed by a sudden surge in demand. Transitioning from a single prototype to a bridge production run of hundreds or thousands of units requires careful planning and robust capacity. A manufacturer's finite resources—including machine availability, skilled labor for setups and finishing, and raw material stock—can create backlogs and frustrate customers if not managed effectively.
To mitigate these challenges, manufacturers must build agility into their operations. This includes:
- Transparent Communication: Clearly stating realistic lead times based on project specifics.
- Predictive Inventory: Stocking common raw materials to reduce procurement delays.
- Efficient Scheduling: Using advanced software to optimize machine utilization and prioritize jobs.
- Supplier Networks: Developing relationships with multiple, pre-vetted manufacturing partners to manage overflow and ensure redundancy.
Ensuring Quality and Supply Chain Reliability for CNC Milling Parts
In on-demand manufacturing, where each part or batch can be unique, ensuring consistent quality is paramount. Unlike mass production where a process is dialed in and repeated, the high-mix nature of on-demand work means quality control procedures must be rigorous and adaptable. Every new design introduces variables that could lead to errors, from programming mistakes to incorrect tool selection. Without a robust quality management system (QMS), defective parts can lead to significant financial losses and damage a manufacturer's reputation.
Key elements of a strong quality control process in on-demand CNC machining include:
- Initial Design Review: Conducting a thorough Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis to identify potential issues before production begins.
- In-Process Inspection: Using tools like CMMs and laser scanners to verify dimensions at critical stages of the machining process.
- Material Verification: Ensuring all raw materials meet the required specifications and have traceable documentation.
- Standardized Procedures: Implementing and auditing standardized work instructions and processes to reduce variability.
Supply chain reliability is equally critical. The on-demand model's success hinges on the timely availability of materials and the dependability of any external partners. A disruption at any point—from a raw material supplier facing shortages to a shipping delay—can halt production and compromise lead times. To build a resilient supply chain, manufacturers should vet suppliers thoroughly, maintain strong communication channels, and potentially diversify their sourcing to mitigate the risks associated with relying on a single vendor.
Leveraging Technology: The Core of On-Demand CNC Milling Parts Manufacturing
Technology is the engine that powers the on-demand manufacturing model. It is the seamless integration of software, advanced machinery, and digital platforms that enables the speed, precision, and flexibility required to succeed. For CNC milling parts manufacturers, harnessing these technological advancements is not just an option but a necessity to stay competitive. From the initial design to the final produced part, a digital thread connects every stage of the process, automating complex tasks, reducing human error, and providing unprecedented control over production.
The Role of CAD/CAM Software in CNC Milling Parts Production
Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) software are the foundational pillars of the on-demand digital workflow. This powerful software duo forms an integrated ecosystem that translates a customer's idea into a physical product with remarkable efficiency and accuracy.
CAD (Computer-Aided Design): The process begins with CAD software, which engineers and designers use to create precise 2D drawings or, more commonly, 3D solid models of a part. These digital blueprints contain every geometric detail, dimension, and specification required for manufacturing. Modern CAD software allows for complex designs, virtual assembly testing, and stress analysis, enabling designers to assess a part's form, fit, and function before any material is cut. This pre-production validation is crucial for identifying potential design flaws early, saving significant time and resources.
CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing): Once a design is finalized in CAD, it is imported into CAM software, which acts as the bridge between the digital model and the physical CNC machine. The CAM system's primary role is to generate the toolpaths—the precise route the cutting tool will follow to shape the part. It calculates optimal cutting speeds, feed rates, and tool angles, then translates these instructions into G-code, the programming language that controls the CNC machine's movements. Modern CAM software also includes advanced simulation capabilities, allowing programmers to run a virtual machining process to detect potential collisions, estimate cycle times, and optimize the toolpath for maximum efficiency and minimal material waste.
This deep integration of CAD and CAM software drastically reduces the potential for human error that can occur with manual programming. It automates complex calculations, ensures an efficient workflow, and brings a high degree of repeatability to the manufacturing process.

Advanced CNC Milling Machines and Their Capabilities
The hardware at the heart of on-demand production is the advanced CNC milling machine itself. Modern machines have evolved far beyond simple three-axis operations and are now equipped with sophisticated features that enable the production of highly complex parts with greater speed and precision.
One of the most significant advancements is the proliferation of 5-axis CNC machining. Unlike traditional 3-axis machines that move along the X, Y, and Z linear axes, 5-axis machines add two rotational axes (A and B). This allows the cutting tool to approach the workpiece from five different directions simultaneously, offering several key advantages:
- Complex Geometries: It enables the creation of intricate shapes, undercuts, and complex contours in a single setup, which would be difficult or impossible on a 3-axis machine.
- Reduced Setups: By machining multiple sides of a part at once, 5-axis machines eliminate the need for operators to manually reposition the workpiece. This drastically reduces setup time, minimizes the risk of human error, and improves overall accuracy.
- Improved Surface Finish and Tool Life: The machine can maintain an optimal cutting angle, resulting in a smoother surface finish and reducing wear on the cutting tools.
Beyond multi-axis capabilities, modern CNC machines are increasingly incorporating automation to enhance productivity and enable "lights-out" manufacturing, where machines can run unattended 24/7. Key automation features include:
- Automatic Tool Changers: These systems can hold dozens or even hundreds of different cutting tools and swap them out automatically as needed for different operations, eliminating downtime.
- Pallet Changers: Automated pallet systems allow multiple raw workpieces to be pre-loaded, so the machine can seamlessly transition from one job to the next without manual intervention.
- Robotic Integration: Robotic arms are used to automate material handling, such as loading raw material into the machine and unloading finished parts, further reducing the need for human labor in repetitive tasks.
These advanced capabilities are essential for an on-demand model, as they provide the flexibility to handle a high mix of complex parts and the efficiency to deliver them with rapid turnaround times.
The Rise of Manufacturing as a Service (MaaS) for CNC Milling Parts
Manufacturing as a Service (MaaS) represents the next evolution in on-demand production, applying the principles of cloud computing and the "as-a-service" business model to the factory floor. MaaS platforms are cloud-based digital networks that connect businesses needing custom parts with a distributed network of vetted manufacturing partners. Instead of owning and operating their own equipment, companies can access a vast array of manufacturing capabilities on a pay-per-use basis.
For CNC milling parts, MaaS platforms revolutionize the procurement process in several ways:
- Instant Access to Capacity: Businesses can tap into a global pool of CNC machines, ensuring they can always find available capacity without being limited to a single supplier. This enhances supply chain resilience and scalability.
- AI-Powered Quoting and Matching: MaaS platforms often use AI-driven algorithms to provide instant quotes based on a customer's uploaded CAD file. The platform then intelligently matches the job to the best-suited manufacturer based on their specific capabilities, experience, and availability.
- Streamlined Project Management: The entire process, from order placement and payment to communication and order tracking, is managed through a single, centralized digital platform. This simplifies supplier management and provides transparency throughout the production lifecycle.
In essence, MaaS democratizes access to high-end manufacturing technology. It allows startups and small businesses to leverage advanced CNC machining capabilities without the massive capital investment, while enabling larger enterprises to optimize their supply chains, reduce lead times, and enhance production flexibility. This model is a key enabler of the agile, responsive, and asset-light approach that defines the future of manufacturing.

Conclusion
On-demand manufacturing, supported by advanced CNC milling, is not just a trend; it's a fundamental shift that empowers businesses, optimizes resources, and drives innovation within the manufacturing industry. By moving away from rigid, forecast-based production and embracing a flexible, order-driven model, manufacturers can meet evolving customer needs with unmatched agility and precision. The benefits—from significant cost and waste reduction to enhanced customization and accelerated time-to-market—provide a powerful competitive advantage in a rapidly changing world.
As a CNC milling parts manufacturer, adapting to on-demand strategies is crucial for staying competitive and delivering exceptional value. It's about combining technological prowess, including sophisticated CAD/CAM software and automated multi-axis machines, with a deeply customer-centric approach. This synthesis is building the future of production—one custom part at a time. SOMI Custom Parts, a CNC milling parts manufacturer from China, offers solutions for CNC milling parts to clients worldwide, embodying this forward-thinking approach. The journey towards on-demand excellence is an ongoing one, and we encourage you to share this article and join the conversation about how these transformations are reshaping your industry.