10 Tips for Choosing the Right Deep Drawn Precision Metal Stamping Supplier
- Share
- Issue Time
- Dec 17,2025
Summary
Selecting a precision metal stamping supplier is crucial for manufacturing success, impacting part quality, cost, and delivery. It's vital to choose a partner whose capabilities align with your production needs to avoid issues like poor precision or delayed deliveries.
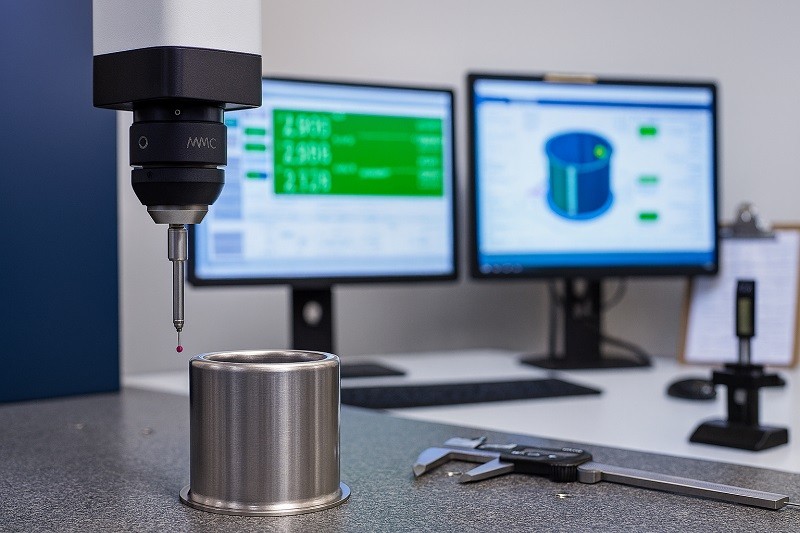

Choosing the right precision metal stamping supplier is a critical decision that can deeply impact the quality, cost-effectiveness, and overall success of your manufacturing process. When you're looking for high-quality metal parts with intricate shapes, the outcome hinges on the skill and capabilities of the partner you select. It is imperative to ensure your chosen precision metal stamping supplier aligns perfectly with your production needs to avoid potential issues like substandard precision, delayed deliveries, or unhelpful after-sales service.
Deep drawn stamping is a specialized metal forming technique that creates components that are deeper than they are wide, resulting in lightweight, seamless parts without sacrificing strength or stability. These components are vital in numerous industries, including medical, automotive, and electronics, for applications like housings, battery casings, and connectors. Given the crucial role these parts play, partnering with an experienced and knowledgeable deep drawn precision metal stamping supplier is essential for ensuring your products function and perform as expected.
Assessing the Technical Prowess of a Precision Metal Stamping Supplier
The foundation of a successful partnership lies in the supplier's technical expertise and the sophistication of their equipment. When choosing a partner, it is paramount to evaluate their machinery, design skills, and material knowledge to ensure they can meet the complex demands of precision manufacturing.
Evaluating Machinery and Equipment
A supplier's equipment roster is a direct reflection of their ability to produce high-quality, consistent parts. Modern, well-maintained machinery is not just a bonus; it's a necessity for achieving tight tolerances and efficient production.
Advanced Stamping Machines and Automation
Reputable service providers should possess state-of-the-art stamping machines capable of handling diverse materials and complex shapes. Servo-driven presses, for example, offer superior control over ram speed and pressure throughout the stroke, which is ideal for complex forming applications requiring high repeatability. This precision helps in achieving better metal flow and shape accuracy.
Automation is another key indicator of an advanced facility. Features like robotic arms for material handling, automatic coil feeders, die changers, and integrated real-time monitoring systems enhance efficiency, reduce manual labor, and minimize downtime. This technology leads to a more consistent and scalable stamping line, ensuring your parts are produced with minimal deviation.
Press Tonnage and Material Range
Press tonnage is the maximum force a press can exert continuously without causing damage to its structure. This is a critical factor, especially when working with high-strength materials or performing deep draws, as the required force must be maintained throughout the process. Hydraulic presses are often preferred for deep drawing because they can deliver full, constant tonnage anywhere in the stroke, unlike mechanical presses where available force decreases further from the bottom of the stroke.
A potential supplier should have a range of presses with varying tonnage capacities (e.g., up to 400 tons or more) to match different material types and part dimensions. Their ability to handle a wide range of materials, from various steels to non-ferrous metals, is also essential. This flexibility ensures they have the right equipment for your specific project, whether it involves simple blanking or complex deep drawing of advanced alloys.
Customization and Design Capabilities
Beyond the machinery, a supplier's engineering expertise is what transforms a concept into a functional, manufacturable part. Their ability to design and fabricate custom tooling and provide collaborative design support is invaluable.
Die Design and Fabrication Expertise
The stamping die is a specialized tool that cuts and shapes sheet metal, and its quality is directly proportional to the quality of the final part. A top-tier supplier should have in-house die design and fabrication capabilities, utilizing skilled die makers and advanced CAD/CAM software. In-house tooling allows for faster adjustments, reduced lead times, and better overall quality control, as the teams responsible for the tool and the production are seamlessly integrated.
Key aspects of die design include calculating the proper clearance between the punch and die (typically 5-10% of material thickness) to ensure a clean cut, and accounting for material springback. An experienced supplier will master these details to produce durable, long-lasting tooling that creates accurate parts efficiently.
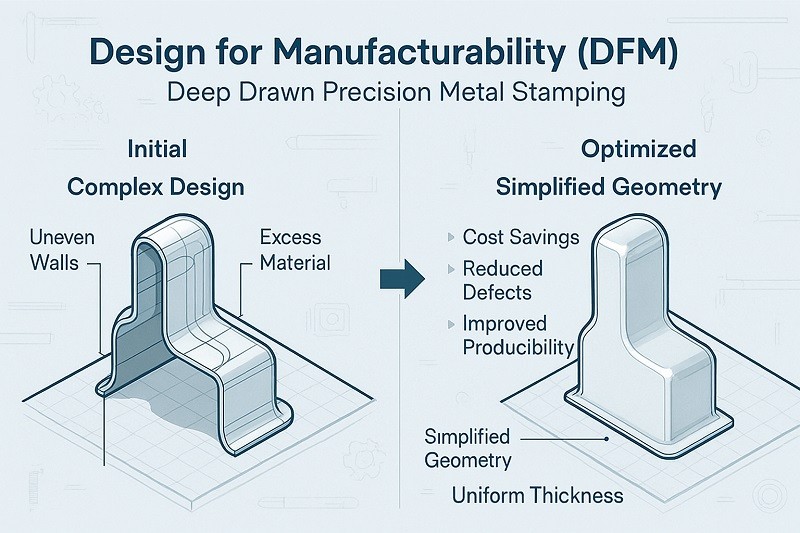
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) and Prototyping Support
Design for Manufacturability (DFM) is a collaborative engineering practice where the part design is optimized for the manufacturing process before production begins. This approach helps identify and resolve potential issues early, which is the least expensive time to make changes. The benefits are significant and include reduced production costs, minimized defects, shorter lead times, and improved overall product quality. A proactive supplier will work with your team to refine designs, suggesting modifications that simplify production without compromising functionality.
Prototyping is another essential service that allows you to test and validate your design before committing to expensive, large-scale production tooling. Many suppliers offer rapid prototyping using techniques like virtual 3D simulations or physical prototypes made with temporary tooling. This step ensures the part meets all specifications and helps identify potential design flaws early in the process, saving considerable time and resources.
Material Handling and Expertise
The choice of material profoundly impacts a part's performance, cost, and manufacturability. An ideal supplier possesses deep knowledge of various materials and can guide you toward the best choice for your application.
Experience with Diverse Materials
Deep drawing can be performed on a wide variety of materials, and your supplier should have proven experience with the one you intend to use. Commonly used materials include:
- Carbon Steel: Available in low, medium, and high carbon grades, it is strong, affordable, and easy to form.
- Stainless Steel: Known for its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and aesthetic finish, making it ideal for medical, food, and marine applications.
- Aluminum: A lightweight, malleable, and corrosion-resistant metal often used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
- Copper and Brass: Chosen for their excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
- High-Strength Alloys: Materials like titanium and nickel-based superalloys are used for specialty components in extreme environments.
A supplier’s familiarity with how different materials behave during the stamping process is crucial for success.
Material Selection Guidance
A great supplier acts as a partner, providing expert consultation on material selection. They should help you balance critical factors such as:
- Application & End Use: The material must withstand the mechanical stresses and environmental conditions of its intended application.
- Formability: Different materials have different levels of ductility and plasticity, which affects how easily they can be shaped without cracking.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The goal is to choose a material that meets performance requirements without being unnecessarily expensive. A knowledgeable supplier can suggest alternatives that balance performance with your budget.
- Availability: The supplier should consider material lead times to ensure your project stays on schedule.
By collaborating with material experts, you can identify an alloy that optimizes performance, manufacturability, and cost.
Ensuring Quality and Reliability from Your Precision Metal Stamping Supplier
Technical prowess is only half the equation. A truly great supplier must also demonstrate an unwavering commitment to quality and reliability. In industries like medical, aerospace, and automotive, where component failure can have severe consequences, this is non-negotiable. Verifying a supplier's quality management systems, performance metrics, and industry reputation is essential to establishing a partnership you can trust.
Certifications and Quality Standards
Formal certifications serve as an objective benchmark of a company's commitment to quality. They indicate that a third-party organization has audited the supplier's processes and confirmed they meet internationally recognized standards.
Industry-Specific Certifications (ISO, IATF, etc.)
When evaluating a supplier, look for key certifications relevant to your industry.
- ISO 9001:2015: This is the most widely recognized standard for quality management systems (QMS). It provides a framework for ensuring consistency and customer satisfaction through documented processes, risk-based thinking, and continuous improvement. A company with ISO 9001 certification has demonstrated its ability to consistently provide products and services that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- IATF 16949:2016: This is a crucial certification for any supplier serving the automotive industry. It builds upon the ISO 9001 framework but includes specific, more stringent requirements for automotive production, focusing on defect prevention, waste reduction, and minimizing variation in the supply chain.
- ISO 13485: This certification is essential for suppliers manufacturing components for the medical device industry. It specifies requirements for a QMS where an organization needs to demonstrate its ability to provide medical devices and related services that consistently meet customer and applicable regulatory requirements.
These certifications are more than just pieces of paper; they prove a supplier has invested in building robust, repeatable systems to ensure quality.
Commitment to Standardized Processes
Beyond certifications, a supplier should be able to demonstrate a deep-seated commitment to standardized processes. This means every job follows established, documented procedures, so the quality of your parts doesn't depend on who is operating the press on a particular day. A robust QMS ensures that from the moment raw materials arrive to the final inspection, every step is controlled, monitored, and verified. This systematic approach is fundamental to preventing defects and ensuring that only high-quality products are shipped.
Well-Defined Quality Control and Objectives
A quality-focused supplier operates with clear, measurable goals. Their quality control program should be an active, data-driven system that monitors every stage of production, not just a final check at the end.
Measurable Performance Indicators
Top-tier suppliers use Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to monitor and improve their processes. When speaking with a potential partner, ask about their performance on crucial quality metrics:
- First Pass Yield (FPY): This measures the percentage of parts that are manufactured correctly the first time without needing rework. A high FPY indicates an efficient and stable production process.
- Defect Rate (PPM): This tracks the number of defective Parts Per Million shipped to the customer. Best-in-class stamping companies aim for a very low PPM rate, often in the single digits.
- Scrap Rate: This KPI calculates the percentage of raw materials that are discarded due to errors. A low scrap rate demonstrates efficient material use and effective process control.
- On-Time Delivery (OTD): This metric gauges the supplier's reliability in meeting deadlines. A consistently high OTD rate (98% or better is a good benchmark) is a sign of strong production planning and logistics management.
A supplier who openly tracks and shares these metrics demonstrates a culture of transparency and evidence-based decision-making.
Traceability and Inspection Practices
Rigorous inspection and traceability are the backbone of quality control. A supplier's process should include several layers of inspection:
- Incoming Material Inspection: Quality starts with raw materials. The supplier should verify that incoming material certifications match specifications for chemistry, thickness, and physical properties before production begins.
- In-Process Inspection: Rather than waiting until a production run is complete, quality teams should perform regular checks during the process. This includes first-article inspections to validate setups and periodic sampling using tools like calipers, micrometers, and Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMMs) to ensure dimensional accuracy.
- Final Inspection: A thorough final inspection is conducted before parts are shipped to verify all specifications are met. Depending on the part's criticality, this may involve 100% inspection or statistical sampling.
Furthermore, complete material traceability is essential, especially in regulated industries. A supplier must be able to track the origin of raw materials and the production history of each part. This capability is critical for containing issues and performing root cause analysis if a defect is ever discovered.

Industry Experience and Reputation
Finally, a supplier's experience within your specific industry and their overall reputation provide invaluable insight into their reliability and expertise.
Specialized Industry Knowledge
A supplier with a proven track record in your industry will already be familiar with its unique standards, regulations, and challenges. For example:
- Automotive: A supplier experienced in automotive will be an expert in the Production Part Approval Process (PPAP), a standardized process for ensuring parts meet all customer engineering design and specification requirements.
- Medical: For medical devices, suppliers must understand the importance of biocompatible materials, extreme cleanliness, and tight tolerances, as a tiny flaw can have significant consequences. They will also be well-versed in the stringent documentation and validation required by bodies like the FDA.
- Aerospace: This industry demands precision, durability, and the use of high-strength, lightweight materials. An experienced aerospace supplier will know how to work with these advanced alloys and meet the sector's rigorous quality standards.
This specialized knowledge ensures that the supplier is not just making a part, but making a part that is compliant and optimized for its final application.
Client References and Testimonials
A supplier's reputation is one of its most important assets. Look for evidence of their performance through case studies, online reviews, and client testimonials. Testimonials from satisfied customers provide social proof and build trust, as they offer an authentic glimpse into how the company solves real-world problems. Don't hesitate to ask a potential supplier for references from companies in your industry. Speaking directly with their current or past clients can provide candid feedback on their quality, communication, and overall reliability, giving you the confidence to build a long-term partnership.
Evaluating Production Capabilities and Support of a Precision Metal Stamping Supplier
A supplier's true value emerges when they can consistently meet your production demands and provide robust support throughout the partnership. Beyond their technical skills and quality systems, you need a partner who can scale with your business, communicate effectively, and offer the flexibility to adapt to changing needs.
Scalability and Production Capacity
A supplier's ability to handle your order volume—both now and in the future—is critical for maintaining a smooth supply chain. This requires a careful evaluation of their production capacity and efficiency.
Handling Varied Order Sizes and Fluctuations
Your production needs will likely fluctuate, ranging from small prototype runs to high-volume production. A capable supplier should have the flexibility to manage both ends of the spectrum. Avoid partners who are operating at over 80% capacity, as this could lead to delays or an inability to handle unexpected rush orders. Conversely, a facility at less than 60% capacity might signal a lack of competitiveness. The ideal partner typically operates at 70-80% utilization, giving them enough spare capacity to be agile. Ask potential suppliers how they allocate resources and manage scheduling to accommodate both large and small orders without compromising lead times.
Efficient Lead Times and Delivery
Lead time—the total time from placing an order to receiving the final product—is a critical metric that impacts everything from inventory costs to customer satisfaction. Shorter lead times allow for leaner inventory management, reduce holding costs, and enable a faster response to market demand. When evaluating a supplier, review their historical on-time delivery (OTD) performance; a rate of 95% or higher is a strong indicator of reliability. Also, inquire about their performance during peak seasons, as this reveals their ability to manage capacity under pressure. A supplier who can maintain consistent lead times even during demand spikes demonstrates robust planning and operational efficiency.
Communication and Customer Service
Effective communication is the foundation of any successful partnership. A supplier who is transparent, responsive, and proactive can prevent misunderstandings, resolve issues quickly, and make you feel like a valued partner rather than just another order number.
Proactive Communication Channels
Look for a supplier that establishes clear and consistent communication channels from the outset. This includes providing a designated point of contact for technical, quality, and administrative questions. A proactive partner will keep you informed about your project's status, share performance metrics, and alert you to any potential issues before they become major problems. Open and honest dialogue builds trust and creates an environment where both parties can collaborate to solve challenges effectively. Avoid suppliers who are hard to reach or provide vague updates, as this can be a red flag for a lack of transparency.
Technical Support and Troubleshooting
A true manufacturing partner does more than just produce parts; they provide expert engineering support to make them better. An accessible and knowledgeable technical team is invaluable for troubleshooting issues, providing design feedback, and offering solutions to unexpected challenges. Look for a supplier that encourages early collaboration, such as through Design for Manufacturability (DFM) reviews, to optimize your part's design for cost and efficiency before production begins. A partner who offers problem-solving workshops or can provide proof-of-principle models to validate solutions demonstrates a deep commitment to your success.
Value-Added Services and Flexibility
A supplier who offers a broad range of in-house services and can adapt to changes provides immense strategic value, simplifying your supply chain and enhancing your agility.
Secondary Operations and Assembly
Many stamped parts require additional processes before they are ready for their final application. A supplier that offers a comprehensive suite of in-house secondary operations can significantly reduce lead times, lower logistical costs, and ensure consistent quality control. These services can include:
- Finishing & Surface Treatments: Plating, powder coating, anodizing, passivation, and electropolishing to improve corrosion resistance or aesthetics.
- Machining & Material Removal: Trimming, deburring, grinding, and tumbling to refine parts and remove sharp edges.
- Heat Treating: Processes to alter the material's physical and mechanical properties, such as increasing hardness or ductility.
- Welding and Assembly: Hardware insertion, spot welding, laser welding, and manual or automated assembly to create sub-assemblies or final products.
By consolidating these processes under one roof, you simplify your supply chain and work with a single point of accountability. This range of capabilities often falls under the larger umbrella of services like Sheet Metal Fabrication, demonstrating a supplier's deep and versatile manufacturing expertise.

Adaptability to Design Changes and Market Demands
In modern manufacturing, change is a constant. Whether driven by product improvements, regulatory updates, or supply chain disruptions, the ability to manage design modifications is crucial. A flexible supplier will have a formal, structured process for handling Engineering Change Orders (ECOs). This process ensures that any proposed modifications are properly reviewed by all stakeholders—including engineering, quality, and procurement—to assess their impact on cost, quality, and timeline. An agile partner can implement these changes efficiently, minimizing rework and preventing costly delays while ensuring that product documentation remains accurate and up-to-date.
Conclusion
Selecting the ideal deep drawn precision metal stamping supplier requires a thorough evaluation of their technical capabilities, quality assurances, and production support. By focusing on their machinery and design expertise, verifying their commitment to quality through certifications and measurable data, and assessing their capacity for scalability and customer support, you can establish a strong, reliable partnership. This careful diligence enhances your production efficiency, reduces risks, and supports your company's long-term growth.
The goal is to find a supplier that not only meets your current project requirements but also functions as a long-term strategic partner. You need a collaborator who offers top-notch metal stamping solutions and comprehensive OEM services. Companies that exemplify these qualities, like SOMI Custom Parts, a dedicated metal sheet fabrication manufacturer, demonstrate the high standards of product quality and partnership that are critical for success in today's competitive market. By applying these tips, you can confidently choose a supplier who will help you achieve your manufacturing goals and drive future innovation.